You might have noticed srsltid parameters appearing in URLs, particularly from Google Search. Originally linked to Google’s auto-tagging feature in Merchant Center, this tracking parameter has sparked discussions about its impact on analytics, SEO, and URL structure. While some believe it could influence ranking signals, others see it as a minor addition with no real consequences.
Around August 2024, users noticed this parameter in their organic search result URLs. The reason behind concerns and debates within the SEO community was that srsltid was not a minor change; this change can represent how Google attributes organic traffic and raises questions about analytical accuracy and SEO best practices.
In this article, we’ll explore its purpose, potential SEO effects, and ways to manage or remove it if necessary.
What is the SRSLTID Parameter, and How Does It Work?
The srsltid parameter, standing for "Search Result Source Listing ID," is a tracking identifier that automatically adds to URLs when users click on specific search results, especially product listings from Google Merchant Center. By adding srsltid, Google tracks user engagement with these listings, helping with performance analysis and optimization.
When you click on a Google Merchant Center product listing, the srsltid parameter appears in the URL. Google uses this parameter to analyze user behavior, such as what search results are clicked on most often and how users navigate various pages.
Example:
Imagine you search for "best web hosting" on Google and click on a result—whether it’s a product listing in Google Shopping or a regular search result. The original URL might be:
https://www.accuwebhosting.com/web-hosting/linux
But after clicking, the URL changes to something like:
https://www.accuwebhosting.com/web-hosting/linux?srsltid=abc123
The srsltid=abc123 part is the tracking parameter. Google uses this to gather insights, but it does not change the actual content of the page.
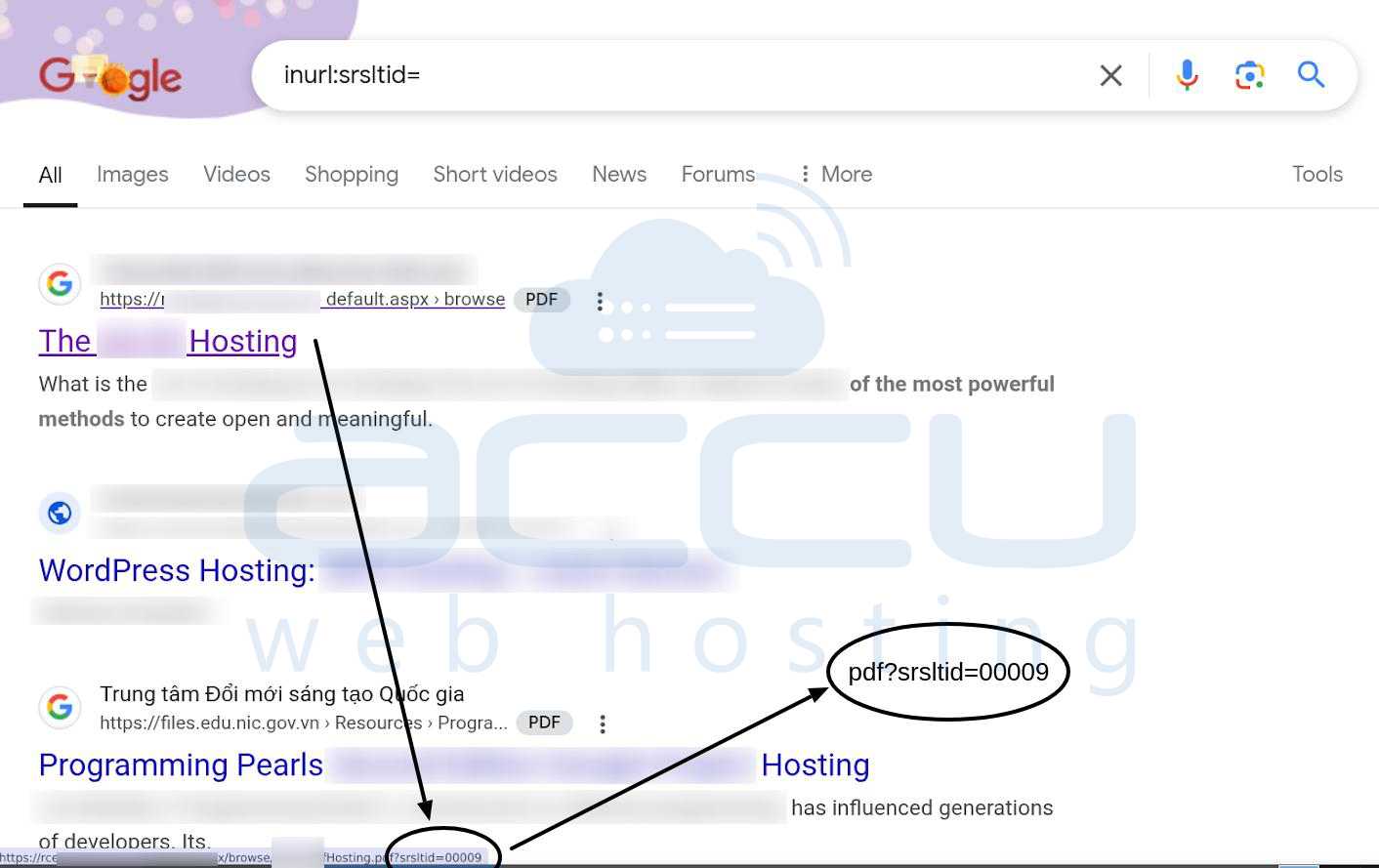
Does Google Index srsltid URLs?
Yes, Google does index URLs with the srsltid parameter. While Google has said this parameter does not affect crawling, indexing, or ranking, actual observations show that Google sometimes indexes these URLs.
A search query like inurl:srsltid= returns millions of indexed pages, showing that Google sometimes considers these URLs separately. This means that without proper management, srsltid URLs can end up in the index, potentially causing duplicate content issues.
Google’s John Muller addresses that srsltid= parameter 'doesn’t affect crawling, indexation or ranking. However, the major issue is that srsltid parameter is generated on each search impression. This means that each time you search something on Google, a new parameter will be added to your URL. This may create hundreds of duplicate URLs of your page and might result in various issues.
How SRSLTID Affects SEO?
Duplicate Content Issues
- Since srsltid creates different URLs for the same page, multiple versions can appear in Google’s index.
- This can weaken a page’s ranking by spreading link value across these duplicates.
- Google may not always merge the signals correctly, which can result in lower rankings for the main page.
- Ironically, this practice directly contrasts with the purpose of the rel=canonical tag, which Google itself recommends to prevent duplicate content issues. When Google generates URL variations with the srsltid parameter, it creates a scenario that canonical tags are designed to resolve.
Keyword Cannibalization
- If Google sees srsltid URLs as separate pages, multiple versions of the same content may target the same keywords.
- This may cause keyword cannibalization, where these similar pages fight for rankings rather than improving the main page's ranking. As a result, the visibility of the primary page may weaken, and search results can become unpredictable.
Crawling and Indexing Inefficiencies
- Googlebot may spend crawl budget on unnecessary variations of the same page instead of focusing on new or important content.
- In some cases, indexing these URLs can clutter Google’s search index with duplicate versions, making site management more difficult.
- Moreover, this change can also impact your website's crawl budget. Googlebot may spend valuable time crawling and indexing these variations of the same page rather than focusing on new or important content. This inefficiency can negatively impact your overall SEO performance.
Impact on Google Search Console & Analytics
- srsltid URLs can create reporting issues in Google Search Console by affecting impression and click data.
- In Google Analytics 4 (GA4), tracking for these URLs is often incomplete, leading to report gaps.
The primary concern is the potential misattribution of organic search traffic to Google Shopping. As the srsltid parameter will be automatically tagged into organic results, the risk is that traffic generated from the standard organic result might be credited to the Google Shopping platform. This could impact eCommerce business owners, relying on accurate data to analyze their campaign effectiveness and take future actions.
Moreover, another issue is that people generally have the tendency to copy the URL from their search bar and share it with others. As these URLs now contain the parameter, they will be shared across the internet, and we can’t stop it. Such a change could drastically impact the analytical data.
How to Handle SRSLTID URLs?
Effectively managing URLs with the srsltid parameter is crucial for maintaining your site's SEO health. Here's how you can handle these URLs:
1. Implement Canonical Tags
Canonical tags help Google identify the main version of a page in cases where several variations are presented based on parameters such as srsltid. Without a canonical tag, Google may index several URLs for the same, and this can create duplicate content issues and decrease the ranking signals.
2. Configure URL Parameter Handling in Google Search Console
Utilize Google Search Console's URL Parameters tool to specify how Google should treat the srsltid parameter during crawling. This helps prevent unnecessary crawling of duplicate pages.
3. Set Up Analytics Filters
In your analytics platform, create filters to exclude the srsltid parameter from URLs. This ensures accurate data by aggregating metrics under the primary URL, avoiding data fragmentation.
4. Regularly Audit Your Site
Perform regular audits to identify and address issues arising from srsltid parameters, such as duplicate content or indexing inefficiencies. This proactive approach helps maintain optimal site performance.
5. Disable Auto-Tagging if Unnecessary
If the srsltid parameter doesn't serve your tracking needs, consider disabling auto-tagging in your Google Merchant Center account. Be aware that this may impact your ability to track specific performance metrics.
Conclusion
The srsltid parameter is a tracking identifier added to URLs, mainly from Google Merchant Center, to track user behavior against product listings. Although Google says it doesn't impact SEO, it can lead to problems such as duplicate content, keyword cannibalization, and crawling inefficiencies, which can affect rankings because Google sometimes indexes these URLs. Site owners need to control them using canonical tags, Google Search Console settings, analytics filters, and periodic audits. If unnecessary, turning off auto-tagging in Google Merchant Center can avoid complexities in tracking and reporting.



