If you're noticing that your computer is running slower than usual, and you do not know the reasons for this sluggish performance, then this article will give you the answers to this slow performance of your Windows computers.
If you've heard about the antimalware service executable in Windows then might be this service hogging your CPU or disk resources, which causes performance degradation. Basically, this component of Windows Defender is designed to offer real-time protection against threats, but it can sometimes consume more system resources than expected.
In this article, we'll dive into why the Antimalware Service Executable can lead to high CPU and disk usage and provide you with step-by-step solutions on how to stop Antimalware Service Executable.
What is Antimalware Service Executable?
The Antimalware Service Executable, also known as "msmpeng.exe", is a background process run by Windows Defender, which is now known as Microsoft Defender Antivirus in newer versions of Windows. This service is responsible for scanning files for malware when accessing them, performing background system scans to check for dangerous software and malware threats, and implementing real-time protection. It ensures that threats are identified and dealt with swiftly.
However, this service can sometimes use a large amount of CPU and disk resources, which might affect the overall performance of your computer. This is typically noticed during full system scans or when updates are being installed.
Why Does Antimalware Service Executable Use So Much CPU and Disk?
There are many reasons that this process can cause high CPU & Disk Usage, and for better understanding reasons are mentioned below:-
>> Full System Scan: When Windows Defender performs a system scan, it can use up a lot of resources.
>> Frequent Updates: Windows Defender constantly checks for updates, which might cause brief spikes in CPU usage.
>> Corrupted Files: If there are corrupted system files, the process may get stuck, consuming excessive resources.
Should You Disable the Antimalware Service Executable?
Deciding whether to disable the Antimalware Service Executable (MsMpEng.exe) is an important consideration that depends largely on your specific circumstances and the security measures you have in place. Here are some points to consider:
Security Risk: Disabling it reduces your system's defenses unless you have another robust antivirus.
Alternative Antivirus: If another antivirus is installed, Windows Defender should turn off automatically.
Performance Concerns: If the service is significantly slowing down your PC, consider disabling it temporarily during high-demand tasks.
Caution: Generally, keep it enabled for continuous protection unless you're sure of your alternative security measures.
Recommendation:
Generally, it's advisable not to disable core security features unless absolutely necessary, especially if no alternative security measures are in place. Regularly update your system and security software to minimize performance issues related to security scans and updates.
How to Stop Antimalware Service Executable?
In this article, we’ll explore three methods to stop or manage the Antimalware Service Executable process. Additionally, we’ll explain six more effective ways to fix this issue without compromising your device’s security. Whether you're looking to temporarily stop the process or adjust settings to optimize your computer's performance, we’ve got you covered.
Method 1. Disable Windows Defender Antivirus (Not Recommended)
Disabling Windows Defender Antivirus will completely stop Antimalware Service Executable from running. However, doing so can make your computer more vulnerable to malware. It's generally not recommended unless you have a third-party antivirus solution in place.
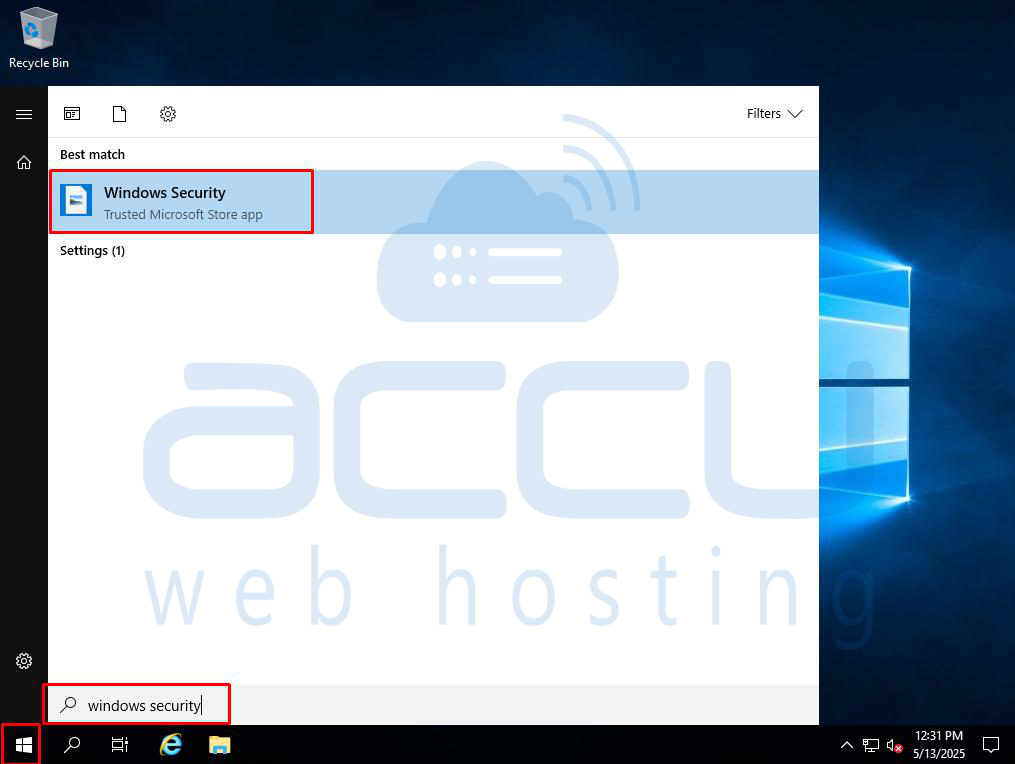
Step 1: Open Windows Security
Press Start and type Windows Security, then click on it.
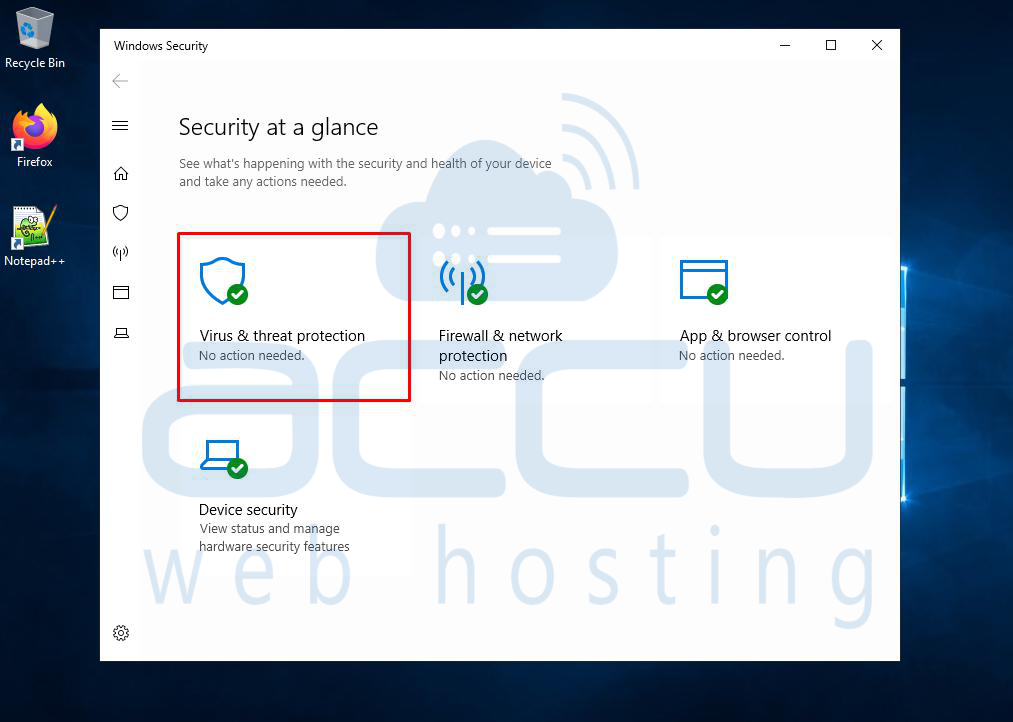
Step 2: Go to Virus & Threat Protection Settings > Manage Settings
Click Virus & Threat Protection, then scroll down to Virus & Threat Protection Settings and click Manage Settings.
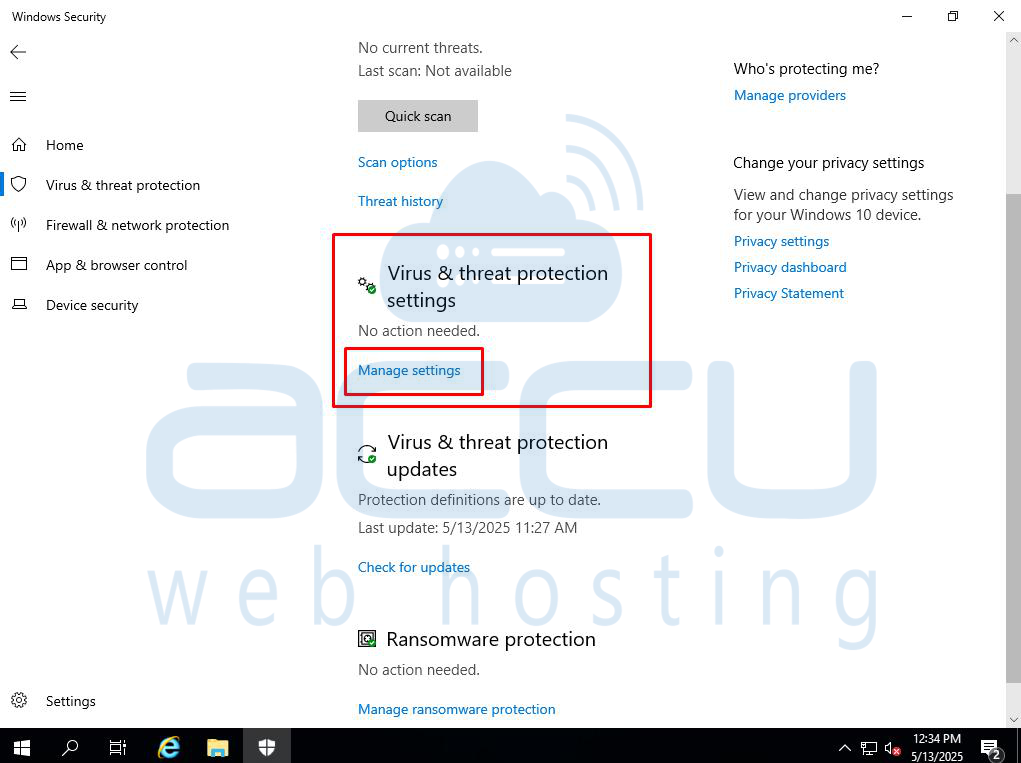
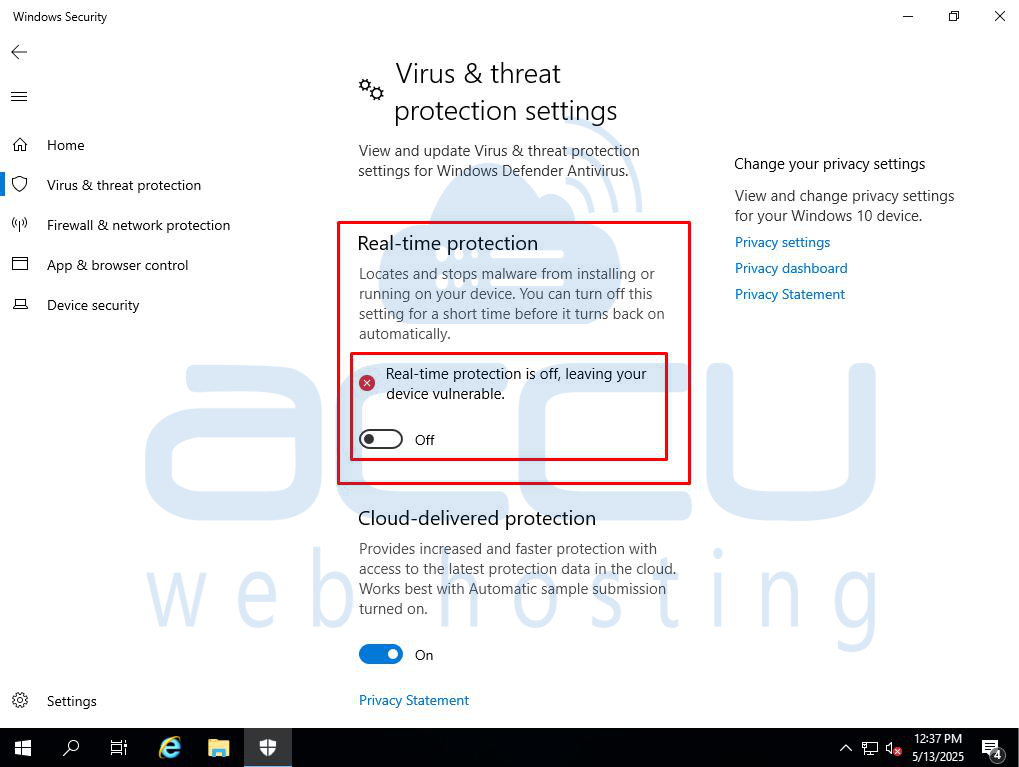
Step 3: Turn Off Real-Time Protection
Windows will turn Real-Time Protection back on after a short period to keep your computer secure.
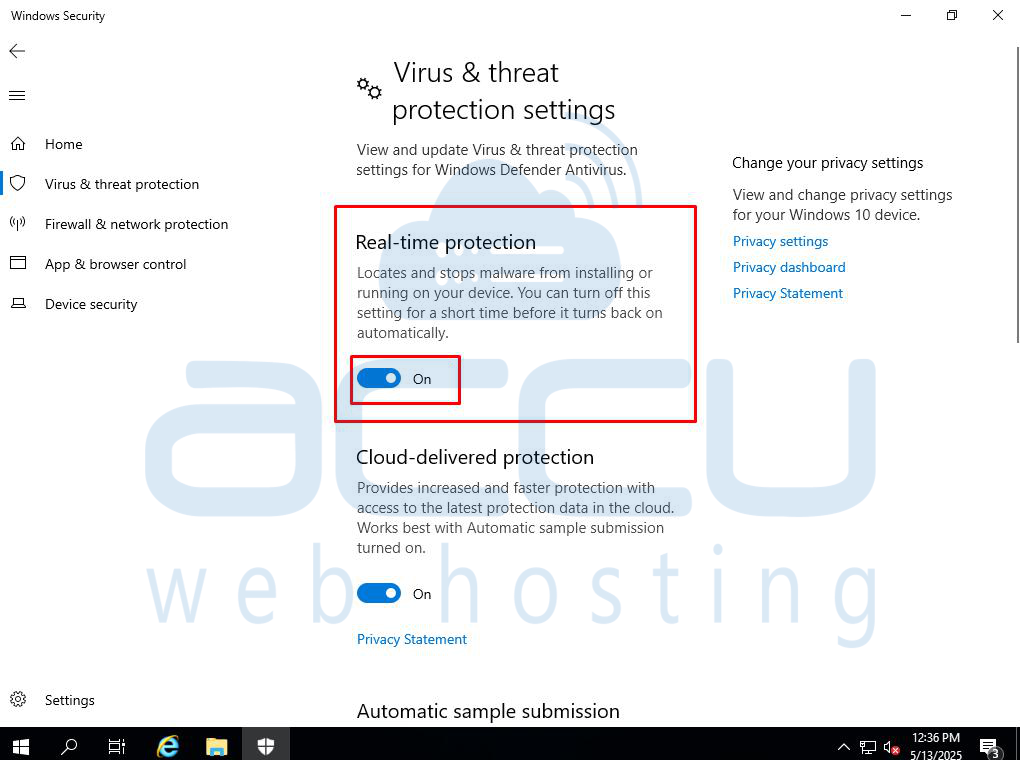
Under Real-Time Protection, toggle the switch to Off. This will stop the Antimalware Service Executable process temporarily.
Step 4: Disable Windows Defender Permanently
If you want to stop Antimalware Service Executable permanently, you’ll need to disable Windows Defender via the Group Policy Editor or Registry Editor.
From Group Policy Editor
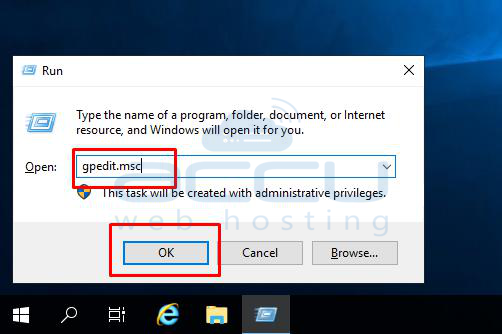
Step 1: Press Windows + R, type gpedit.msc, and press Enter.
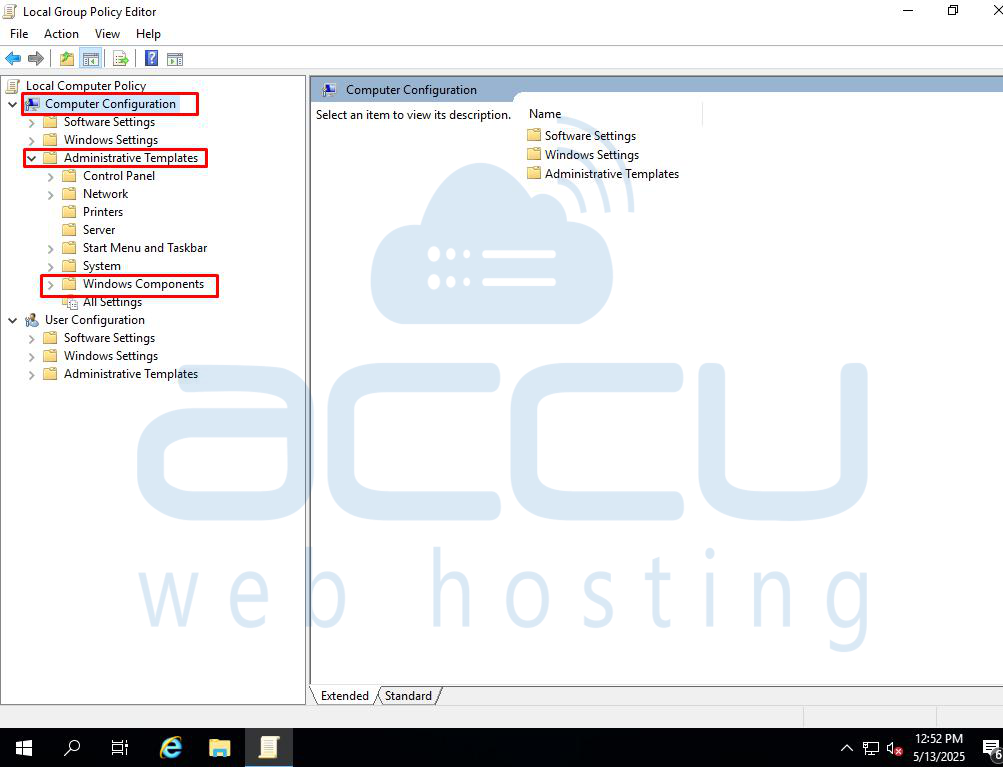
Step 2: Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Defender Antivirus.
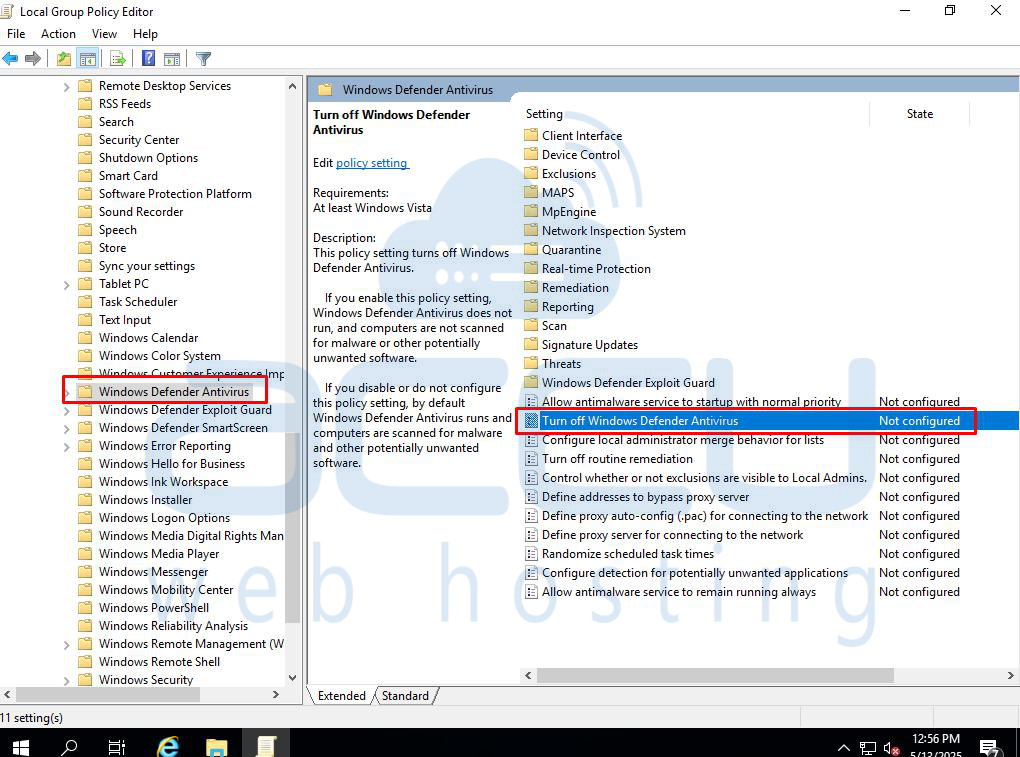
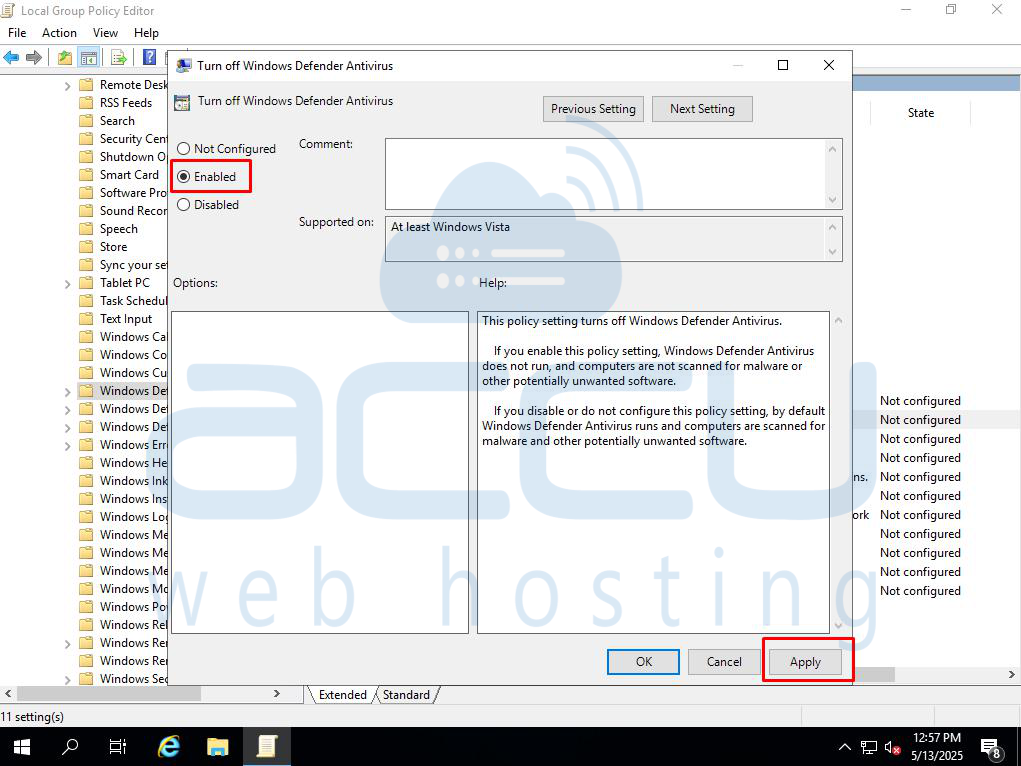
Step 3: Under Windows Defender Antivirus, double click on “Turn off Windows Defender Antivirus.”
Step 4: Select Enabled, and click Apply.
Method 2. Disable Windows Defender Service
If you want to stop Antimalware Service Executable but prefer not to disable Windows Defender entirely, you can stop the Windows Defender service via Services. This will prevent the service from running in the background, which in turn stops the process.
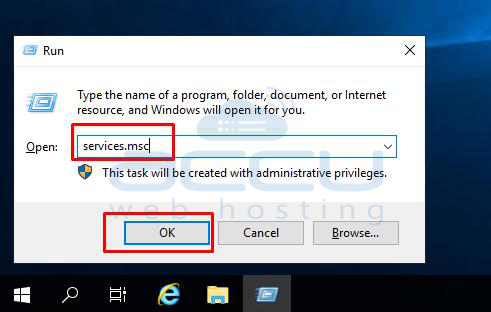
Step 1: Open Services
Press Windows + R, type services.msc, and press Enter.
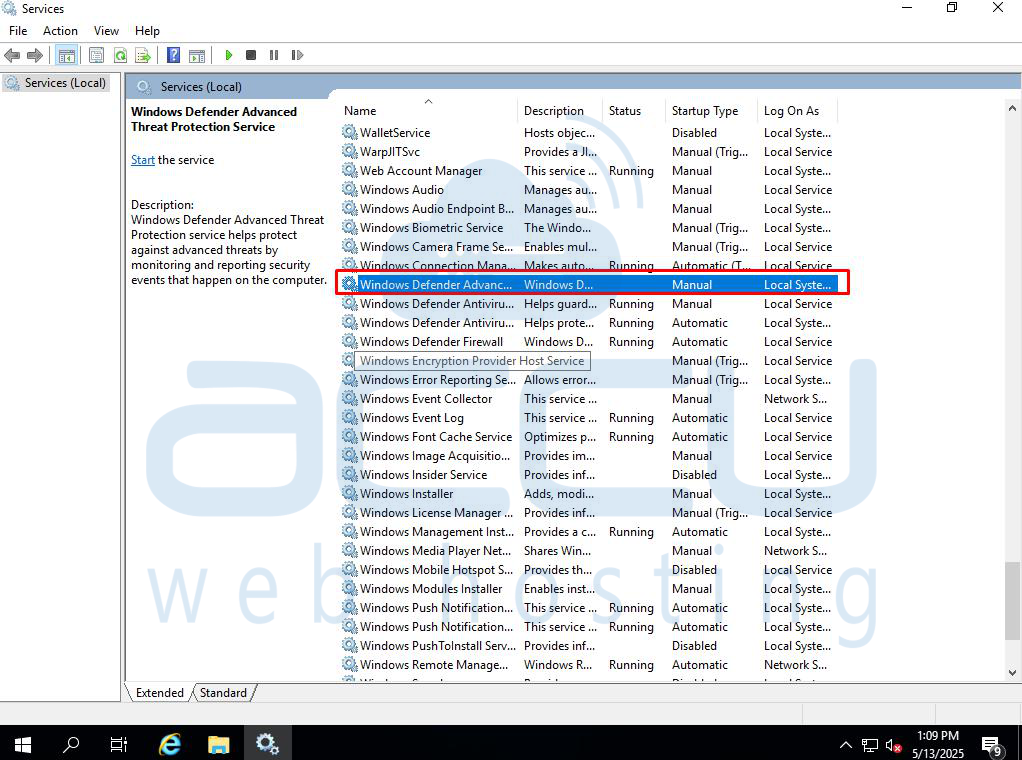
Step 2: Find Windows Defender Antivirus Service
In the "Services" window, find and double-click on "Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection service.”
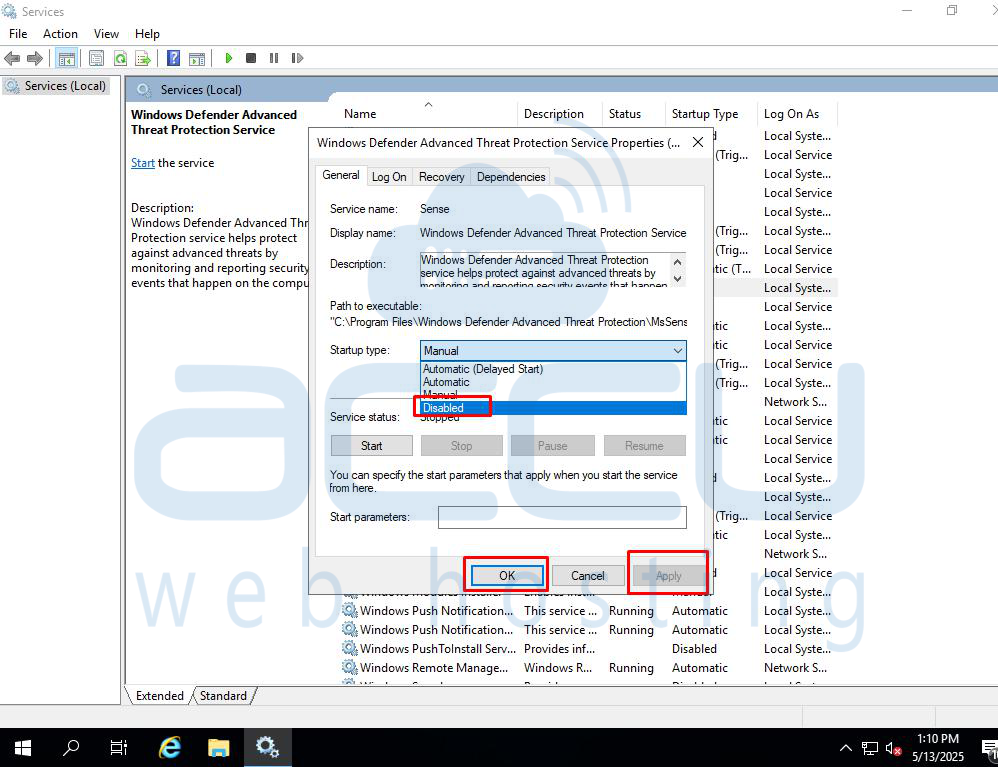
Step 3: Stop the Service or Set the Service to Disabled
In the "Properties" window, set the "Startup type" to "Disabled," then click "Apply" and "OK."
Restart your computer to apply the changes.
Conclusion
Disabling the Antimalware Executable Service (MsMpEng.exe) on Windows Server is a straightforward process via Group Policy. This should only be done in controlled environments, typically when another antivirus program is in use. While it can reduce CPU usage or resolve compatibility issues, it also removes a layer of defense against malware, so weigh the security implications carefully before proceeding.



