GeoIP refers to the process of identifying the geographical location of an IP address. It uses databases to map IP addresses to specific locations, which may include the country, region, city, or even latitude and longitude.
To install GeoIP on a Linux server, follow these steps:
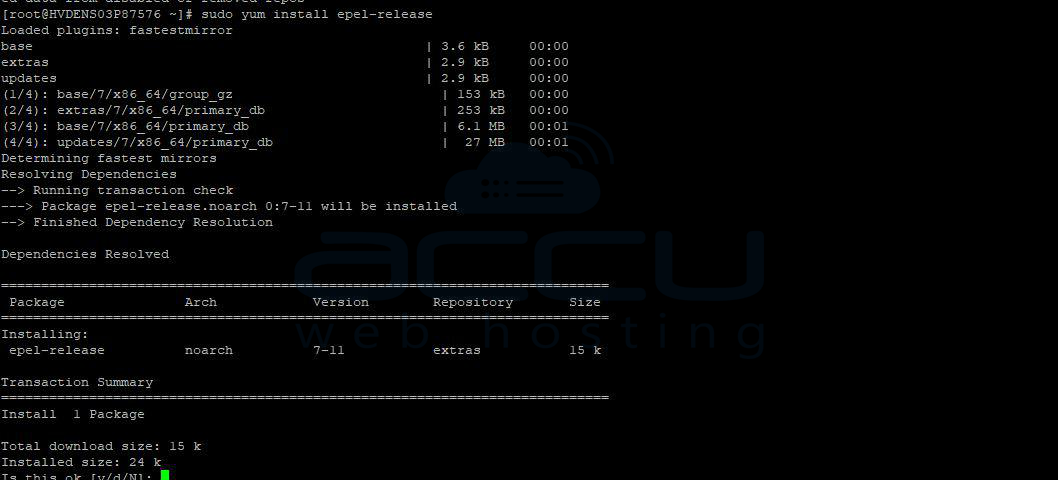
Step 1. Update Your Server Packages
- For Debian-based distributions (like Ubuntu):
- For Red Hat-based distributions (like CentOS):
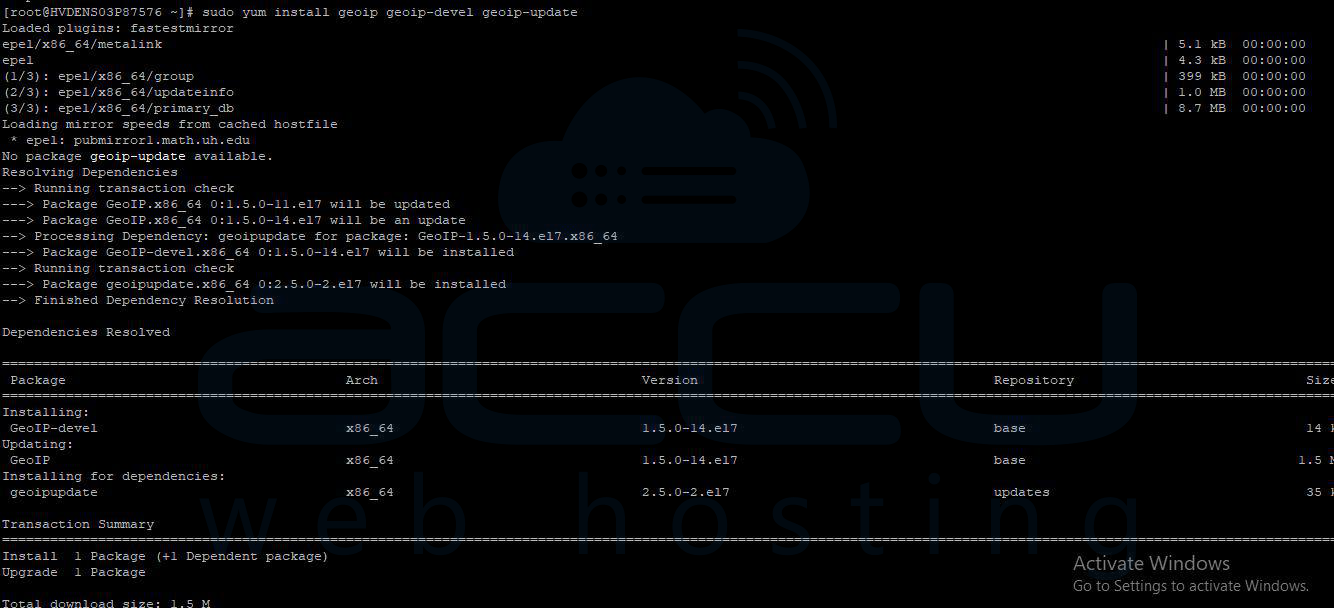
Step 2. Install GeoIP Library and Development Files
- For Debian-based distributions:
- For Red Hat-based distributions:
Step 3. Download GeoIP Database Files
- Use `wget` to download the GeoLite2 databases from MaxMind:
Step 4. Extract and Move Database Files
- Extract the files:
- Move them to the GeoIP directory:
Step 5. Configure GeoIP
- Create or edit the GeoIP configuration file:
- Add the following lines:
Step 6. Set Permissions
- Ensure proper permissions for the GeoIP directory and files:
Step 7. Test the Installation
- Use the geoiplookup command to verify the setup.
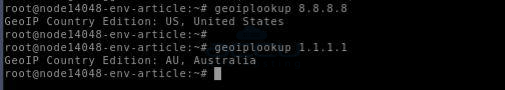
Conclusion:
To install GeoIP on a Linux server, use the package manager of your distribution to install the necessary packages (for example, apt for Debian/Ubuntu or yum for CentOS/RHEL). After that, update the GeoIP configuration file with your account information and configure GeoIP by acquiring a MaxMind license key. Run geoipupdate after setup to obtain the most recent GeoLite2 databases. Lastly, check the installation with GeoIP2's geoiplookup. With this configuration, web servers, firewalls, and analytics tools can use IP-based geolocation.



