IPMI is a hardware-based solution for securing, controlling, and managing servers. It refers to a set of computer interface specifications used for out-of-band management. Out-of-band refers to accessing a computer system without being in the same room as the system's physical resources. It supports remote monitoring and does not require permission from the computer's operating system.
Features of IPMI
IPMI is a software-agnostic approach that works independently of the server's BIOS, CPU, and operating system. The main reason IPMI is so important is that it can effectively perform four functions:
-> Server monitoring
-> Server restore and reboot
-> Log server state
-> List all server inventory
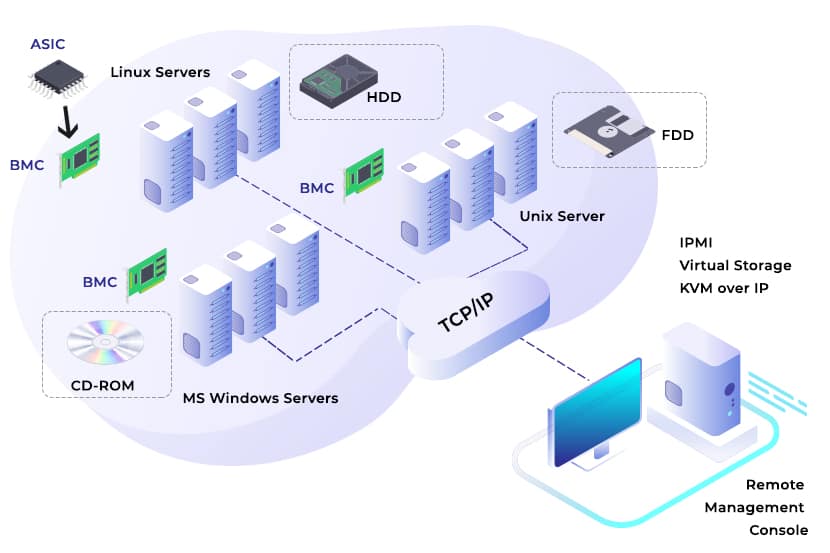
Advantages of IPMI
A major advantage of IPMI is that it allows system administrators to remotely perform various monitoring and management tasks, such as RPM and temperature, without having physical contact to the system and connect to it. In a modern data center, where there may be hundreds of racks or thousands of servers, it's impossible without it. Therefore, all modern servers and other equipment (switches, storage devices, power supplies, etc.) used in data centers are all IPMI-enabled. Other important benefits are:
Predictive monitoring - Unexpected server failure causes downtime. Downtime disrupts business operations and can cost companies up to $250,000 an hour. IPMI tracks server status and provides advanced alerts on potential system failures. IPMI monitors predefined thresholds and issues alert when exceeded. Therefore, actionable IPMI intelligence helps reduce downtime.
Independent Intelligent Recovery - In the event of a system failure, IPMI will recover and get you back up and running. Unlike other server monitoring tools and software, IPMI is always accessible, facilitating server recovery. IPMI helps recover from situations where the server is powered off.
Vendor-agnostic universal support — IPMI is independent of proprietary hardware. Most hardware vendors have integrated IPMI support to eliminate compatibility issues. IPMI extends its server monitoring capabilities into a multi-vendor hardware ecosystem.
Agentless Management - IPMI manages the server's operating system without relying on agents. This allows you to adjust settings such as the BIOS without logging into the server's operating system or obtaining permissions.
Disadvantages of IPMI
Using IPMI comes with risks and some drawbacks. These drawbacks focus on security and usability. The user experience shows the following weaknesses:
Cybersecurity Challenges - The IPMI communication protocol can leave loopholes that cyberattacks can exploit, and statistics show that successful breaches are costly. The IPMI installation and configuration procedures used can also make dedicated servers vulnerable and susceptible to attack. Due to these security challenges, encryption and firmware firewall features were added to IPMI version 2.0.
Configuration Challenges - The task of configuring IPMI can be daunting in situations with sparse legacy network setups. In such cases, clearing the network configuration using the system's BIOS can resolve any configuration issues encountered.
Update Issues – Installing update patches can cause network outages. Changing motherboard ports may cause malfunctions. In such situations, rebooting the system can resolve the issue that caused the network to go down.



