Losing important data due to hardware failures can disrupt business operations. RAID 10 offers a reliable solution by combining data redundancy and performance. This configuration ensures fault tolerance, allowing the system to continue functioning even if multiple drives fail, as long as they are not part of the same mirrored pair. This article explains RAID 10's fault tolerance capabilities in detail.
What is RAID 10?
RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0, combines the features of RAID 1 (mirroring) and RAID 0 (striping) to enhance both data redundancy and performance. It requires a minimum of four disks, where data is mirrored across pairs for redundancy and striped across these pairs for improved speed.
This configuration offers high read/write speeds and quick recovery from disk failures, making it ideal for applications requiring reliable and fast data access, such as databases and servers
If you want to learn more about RAID levels and how they work, check out this blog.
Why RAID 10 is a Reliable Choice for Fault Tolerance
RAID 10 is a reliable choice for fault tolerance because it provides both redundancy and performance. The mirrored drives ensure that even if one drive fails, the data remains accessible from the other mirror. This setup allows the system to continue functioning without data loss as long as the failure doesn't occur within the same mirrored pair.
The striping aspect enhances performance, speeding up data access and improving overall system efficiency. This combination of high availability and fast recovery from drive failures makes RAID 10 a top choice for environments where data protection and reliability are critical.
Fault Tolerance in RAID 10
The fault tolerance of a RAID 10 array depends on its configuration:
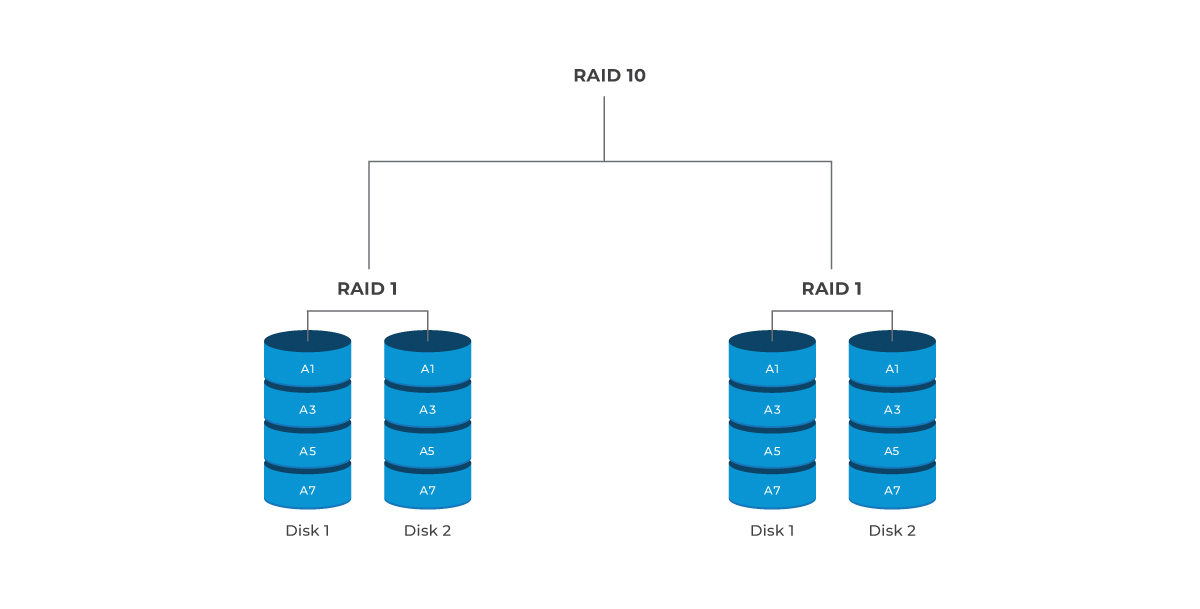
4 Drives: The array consists of two mirrored pairs. It can tolerate one drive failure from each pair, allowing for a maximum of two drives to fail without data loss, provided they are from different pairs. If both drives in one mirrored pair fail, all data in that pair will be lost.
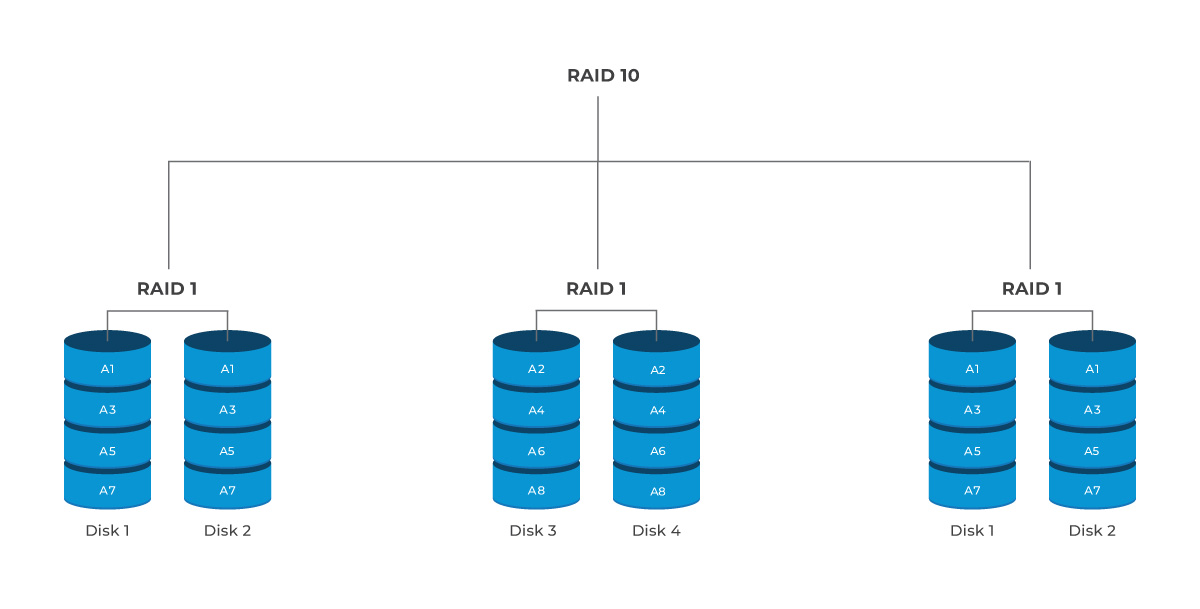
6 Drives: With three mirrored pairs, the array can sustain up to three drive failures, again, as long as no two failures occur in the same mirrored pair.
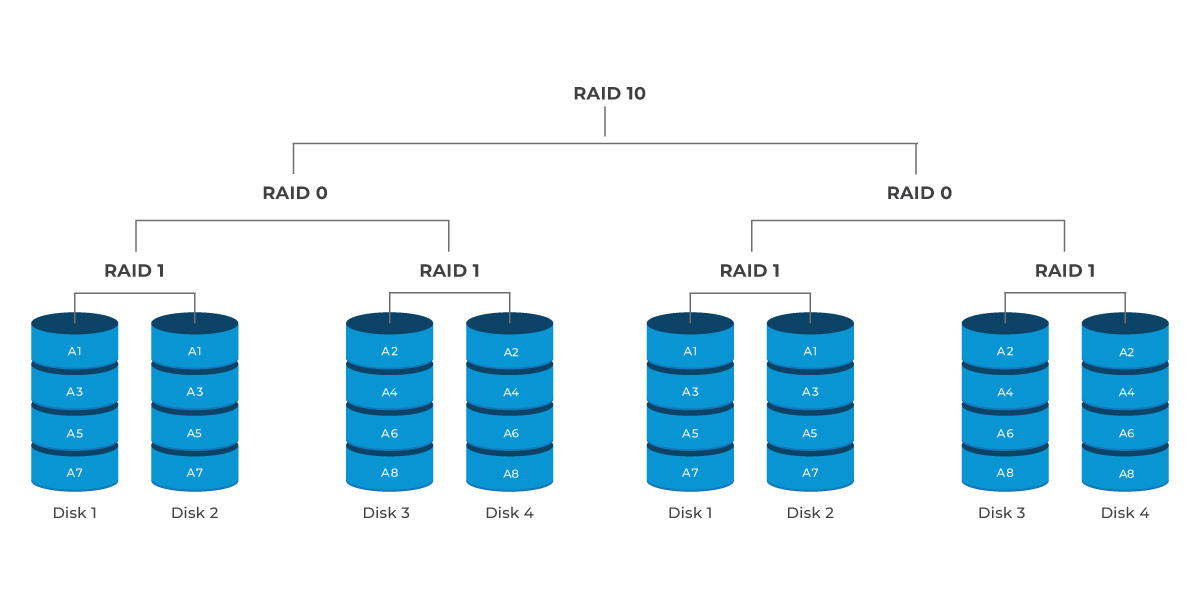
8 Drives: This configuration allows for four drive failures, with the same condition regarding the mirrored pairs. The risk of data loss increases significantly if two drives from the same pair fail simultaneously.
Key Features of RAID 10
Enhanced Data Protection
RAID 10 ensures strong data protection by mirroring data across multiple drives. If one disk fails, the data remains safe and accessible, maintaining high system availability and reliability—essential for web hosting environments.
Improved Performance
RAID 10 boosts performance by distributing data across several disks through striping. This enhances read and write speeds, making it ideal for applications that require quick and frequent data access.
High Fault Tolerance
RAID 10 offers strong fault tolerance, allowing the system to handle multiple drive failures without losing data, provided that no two drives from the same mirrored pair fail. This exceptional level of fault tolerance is critical for maintaining uptime in essential systems, particularly in managed hosting environments and cloud services, where continuous availability is crucial.
Easy Recovery
RAID 10 arrays are designed for quick recovery. When a drive fails, it can be replaced with a new one, and the array will automatically rebuild the data onto the new drive using the mirrored copy. This automatic rebuild process minimizes downtime and ensures the system remains operational during the recovery. The simplicity of the recovery process is a significant advantage, especially for businesses that require high availability.
RAID 10 offers robust data protection through its unique combination of mirroring and striping, making it suitable for environments where data availability is critical. While it provides high fault tolerance, users must be aware of the limitations regarding simultaneous drive failures within mirrored pairs to effectively manage their storage solutions.



