The RDP error 'An internal error' commonly arises from alterations to RDP settings or local group policy security. We have received multiple reports from clients citing complications with RDP.
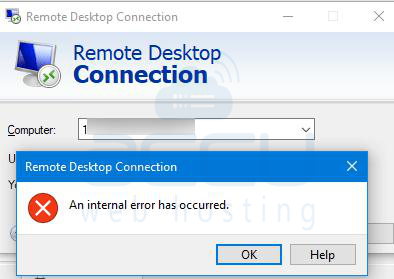
The potential causes of this problem may include RDP connection settings, RDP security, or domain-related issues with the computer. We have compiled a detailed list of possible solutions and step-by-step instructions to address this issue.
Solution 1: Verify Remote Desktop Connection Settings
Changing the RDP setting a bit may fix your issue. So you can try the below.
1. Go to Start >> Run. Type the mstsc command and hit enter button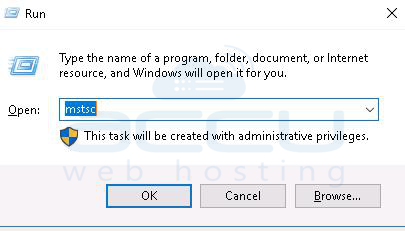
2. Expand the Show Options button. It will give you some buttons in the same dialogue box. Click on the Experience tab to ensure that "Reconnect if the connection is dropped" is ticked.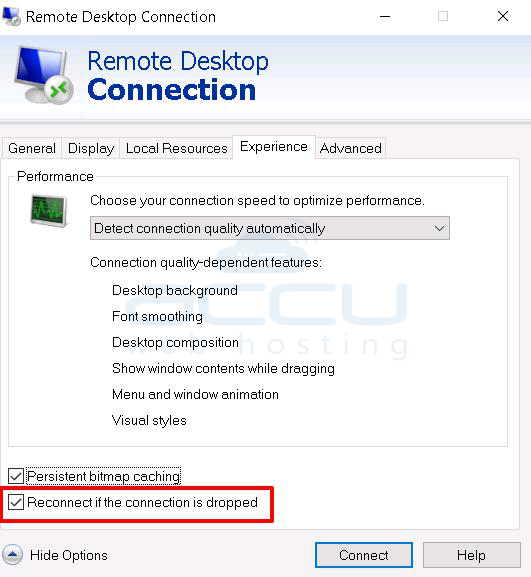
3. Try to connect the RDP again.
Solution 2: Disabling Network Level Authentication
If Network-level authentication is enabled, the machine can only connect to the remote connection running with NLA. You can disable it and try to connect again.
1. Click on Remote settings >> RDP tab.
2. Untick the Allow connection only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication (recommended)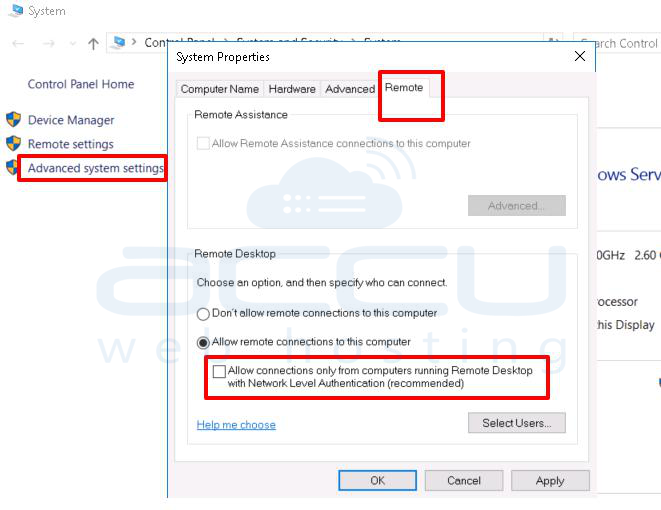
3. Click on the OK button.
Solution 3: Restart Remote Desktop Service
1. Go to start >> Run and type Services.msc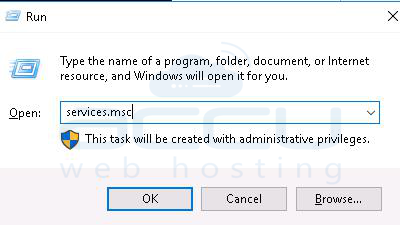
2. At services, Select Remote Desktop Services and restart it.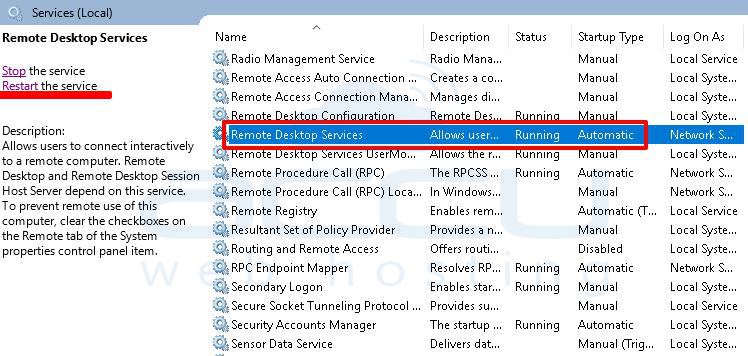
Solution 4: Allow Remote Connections
1. Right-click on my computer and click on properties.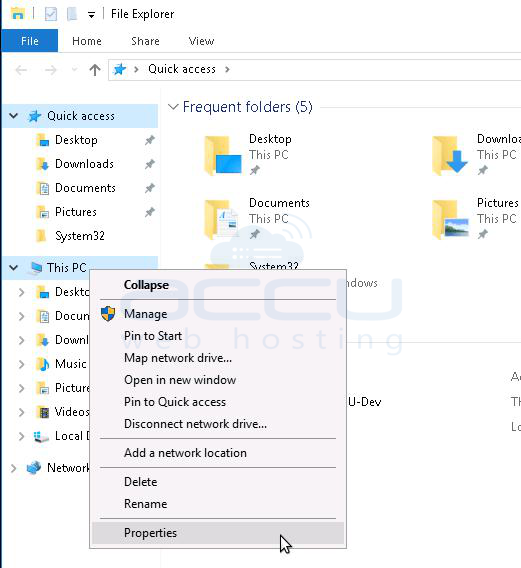
2. Click on advanced system settings >> Remote.
3. Make sure allow remote connection to this computer is checked.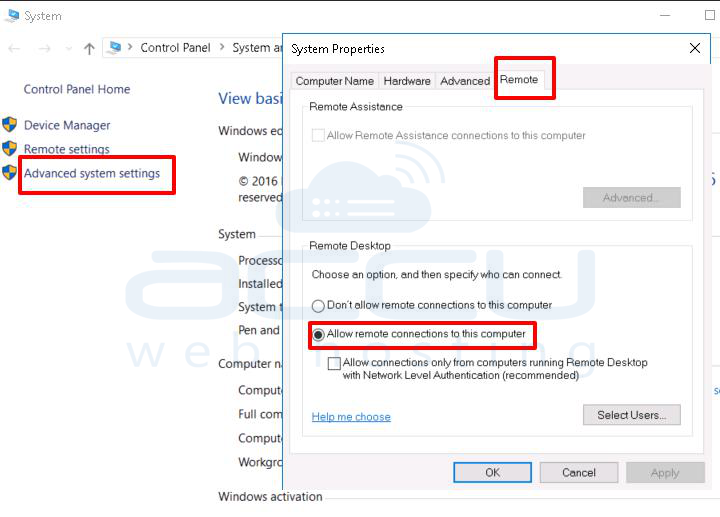
Solution 5: Change the Security of RDP in the Group Policy Editor
Change the RDP security in group policy; that may fix your issue.
1. Go to Run and type gpedit.msc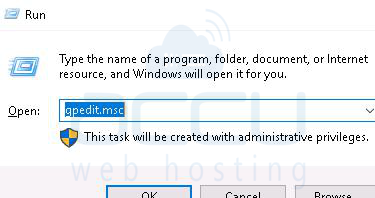
2. Click on advanced system settings >> Remote.
3. Navigate to the directory. Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Security
4. Right-click on Require use of specific security layer for remote (RDP) connections and select the edit button.
5. Tick to enable button. It will set RDP at the Security Layer.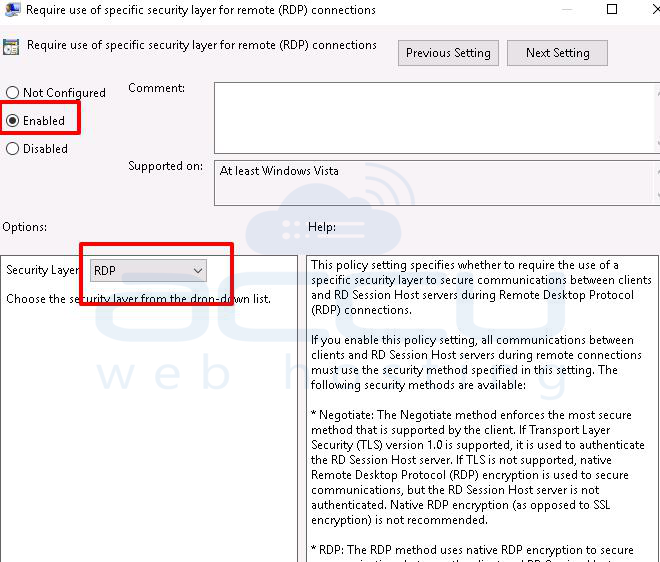
6. Hit the OK button and restart your machine.
Solution 6: Disable VPN Settings
1. Go to Run and type inetcpl.cpl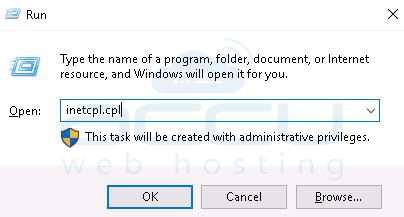
2. At the Internet option, click on the connections button.
3. Click on the LAN Settings button.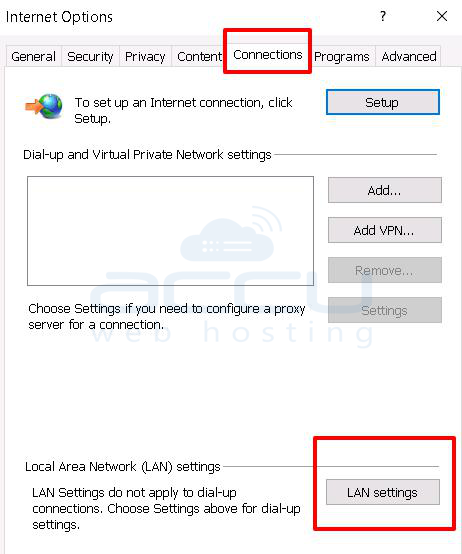
4. Untick the use proxy server checkbox.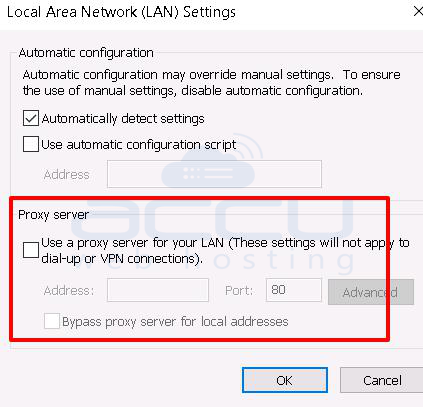
5. Restart the machine and check again.
Solution 7: Modify the Local Security Policy
You can modify your machine's local security policy, which can be one of the fixes for your RDP issue.
1. Go to Run and type Secpol.msc
2. Go to Local policies >> Security Options
3. Scroll down and find the policy: System cryptography: Use FIPS compliant cryptographic algorithms, including encryption, hashing and signing algorithms option.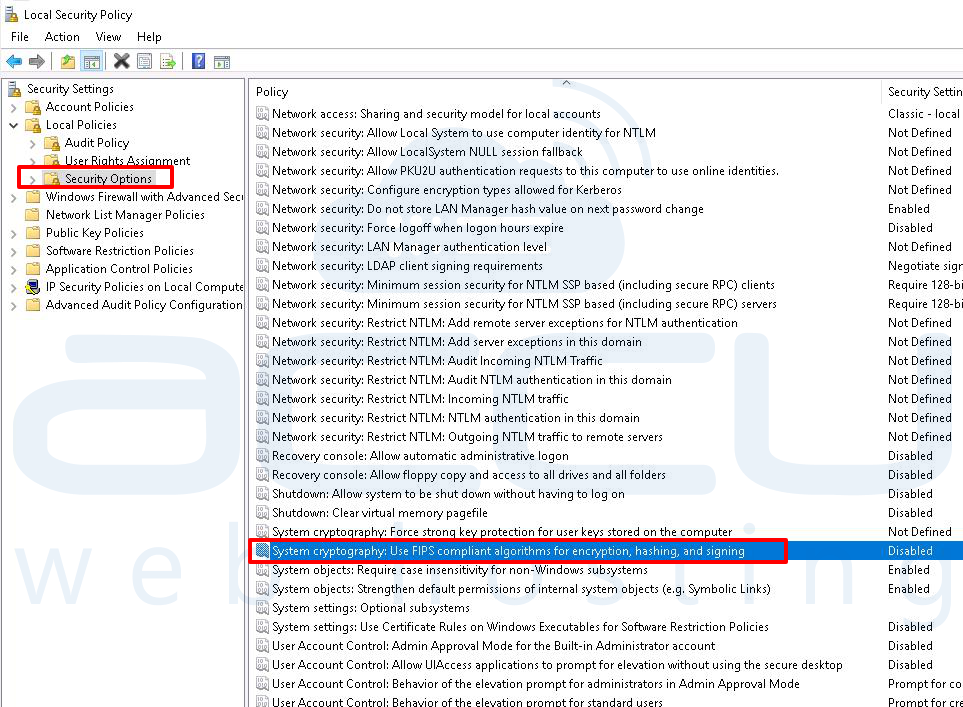
4. Restart the machine and check again. Double-click on it and tick on Enable.
5. Click on Apply and OK Button.
6. Restart your machine, and that should fix your issue.
Solution 8: Change the Startup of the Service
You can set the Remote Desktop service startup type to "automatically".
1. Go to Run and type services.msc
2. Find Remote Desktop Services. Right-click and select properties.
3. At startup type, select Automatic from the drop-down and hit the OK button.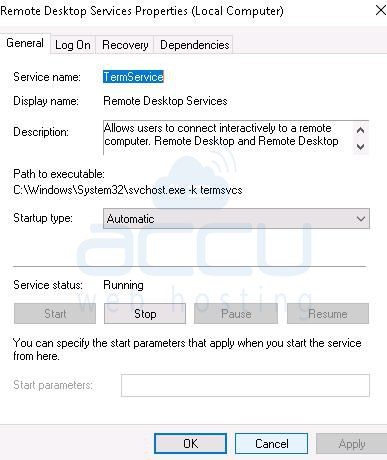
4. Check the RDP connection and try again.
Solution 9: Allow the Firewall to connect to RDP
The default port for the RDP is 3306, but if you have configured your RDP to work on other than 3389, then you will need to add the same port in the windows firewall.
1. Go to start >> Administrative tools and open Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
2. Click on Inbound Rule >> New Rule >> select port >> Specify new port.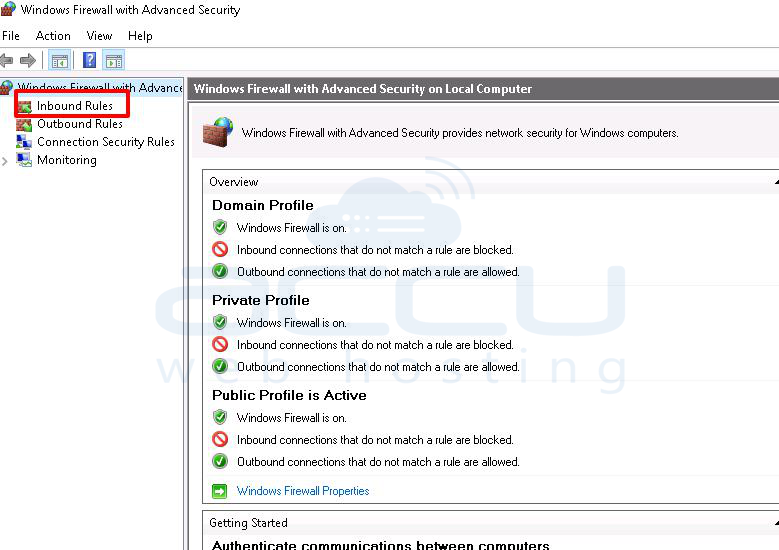
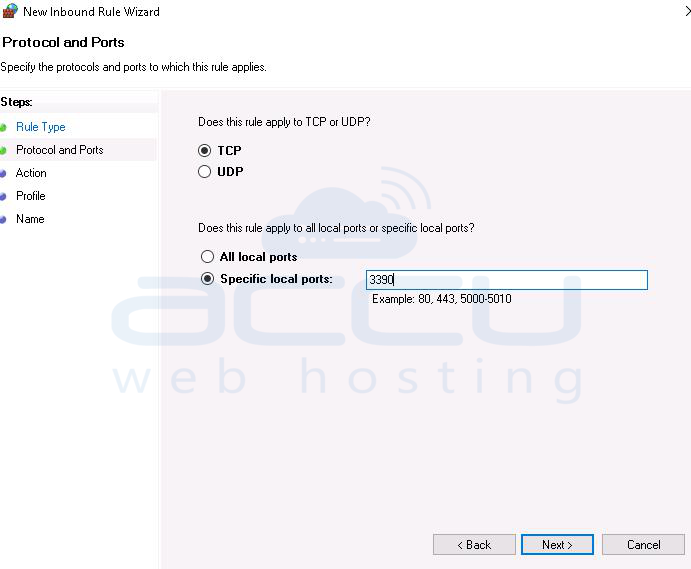
3. Allow the connection to Domain, private and public.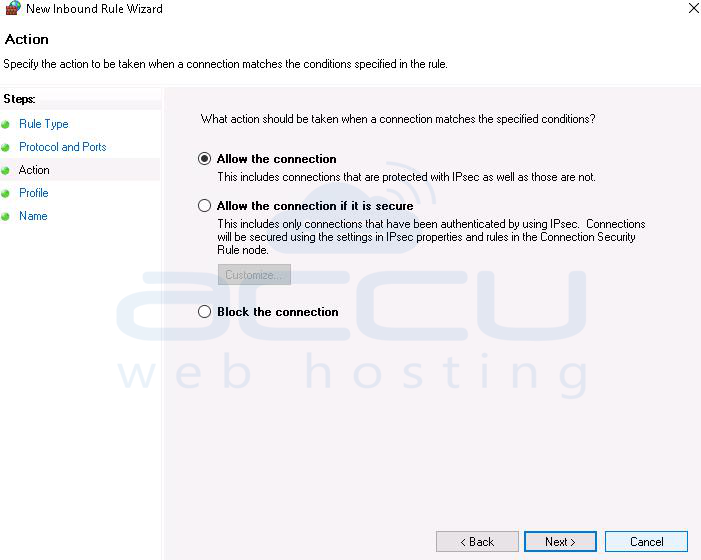
4. Give the name of your rule and hit the finish button.
5. If you have set another Port for the RDP, your issue should be fixed by now.
Solution 10: Change MTU Value
MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) is the value of packet size that can be sent via the Network. Changing the MTU value may fix your issue.
1. You can change the MTI value from the TCP optimizer. Download the TCP Optimizer from this link.
2. After downloading TCP Optimizer, open it as administrator.
3. At the bottom of the dialogue box and tick on custom.
4. Modify the MTU value to 1458.
5. Click on Apply change and Exit.
6. Connect your machine now.
Solution 11: Persistent bitmap caching
1. Go to Run and type mstsc.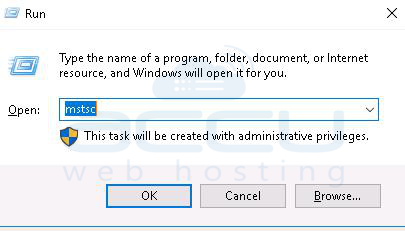
2. Click on Show Options.
3. Click Experience Tab >> Tick on the Persistent bitmap caching.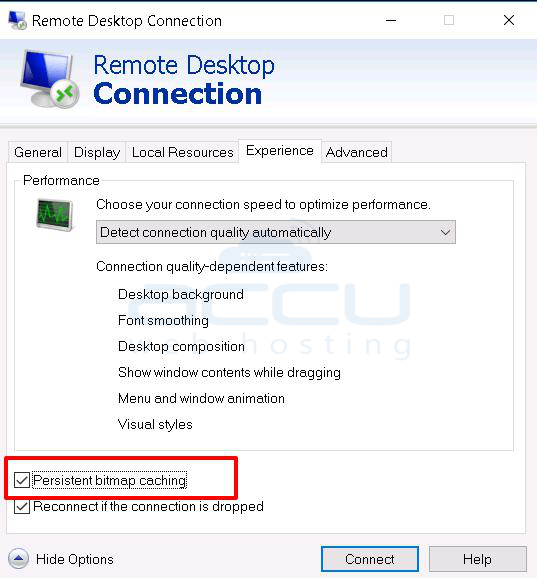
4. Try to connect your system now.



