HTTP, which stands for hypertext transfer protocol, is a fundamental part of most websites.
It's basically how computers and servers communicate to ask for and share information. For example, when you go to a website like
Accuwebhosting.com, your web browser, sends a request to Accuwebhosting's servers to get the content for the page. The servers then respond with your browser's text, images, and layout.
What is HTTP/1.1?
Now, let's discuss HTTP/1.1. It's the first version of HTTP, created in 1997, and it's still used on the Internet today.
What is HTTP/2?
In 2015, a newer version called HTTP/2 was introduced. HTTP/2 is an improved version that makes things work faster and more efficiently than HTTP/1.1.
One cool thing about HTTP/2 is how it handles content loading, making the whole process quicker.
What does prioritization mean?
In web performance, prioritization is about deciding the order in which different parts of a webpage load. Imagine you're on a news website reading an article. Should the pictures load first? Or maybe the text of the article? What about banner ads?
The order in which things load can affect how fast the webpage appears. For example, big files like JavaScript might slow down the page if they have to load first. But if these files load last, more pages can appear quickly.
The order also affects how users see the page loading. If things that are not immediately visible (like a CSS file or ads at the bottom) load first, users might think the page isn't loading. But if the most important stuff, like the main image, loads first, users feel the page loads faster.
How does prioritization work in HTTP/2, and why does it make things faster?
- In HTTP/2, developers have extensive control over the order in which different parts of a webpage load.
- This control helps make the webpage appear to load faster, which was not possible in the older version, HTTP/1.1.
- HTTP/2 has a feature called weighted prioritization. This lets developers choose which parts of a webpage load first every time.
- In HTTP/2, when you request a webpage, the server sends several sets of data to you all at once instead of sending them one by one. This method of sending data is called multiplexing.
- Developers can give each data set a different value, which tells your computer which data to show first.
What are the main differences between HTTP/2 and HTTP/1.1 that affect how fast they work?
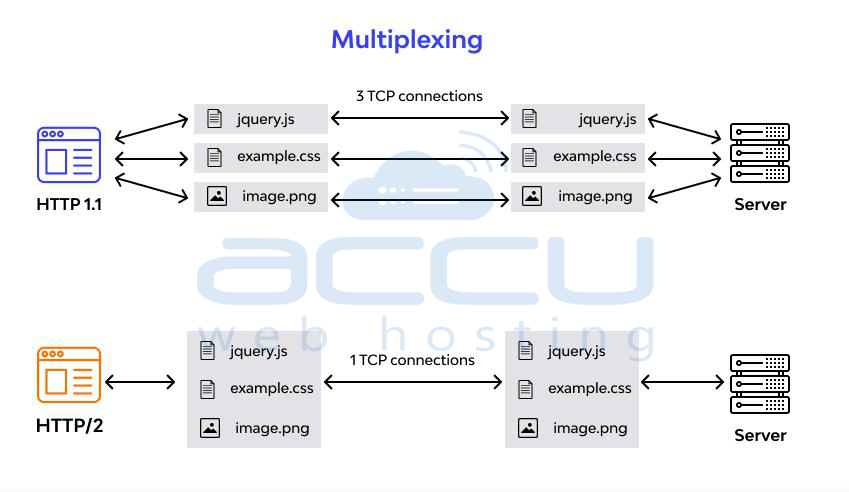
Multiplexing:
- In HTTP/1.1, things like pictures or text load one after another.
- If one thing can't load, it stops everything else behind it. But in HTTP/2, it can send many sets of data at the same time using just one connection.
- This means if one thing can't load, it doesn't stop the others. It does this by breaking data into messages in a unique code and giving each message a number so your computer knows what goes where.
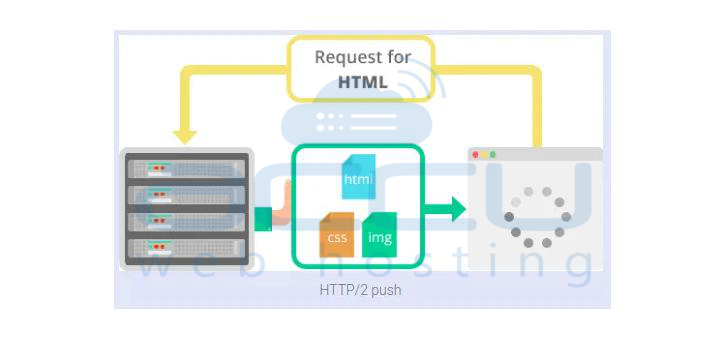
Server push:
- Usually, a server only gives stuff to your computer if it asks.
- But modern web pages have many things, and asking for each can be slow.
- In HTTP/2, the server can send things to your computer before it even asks.
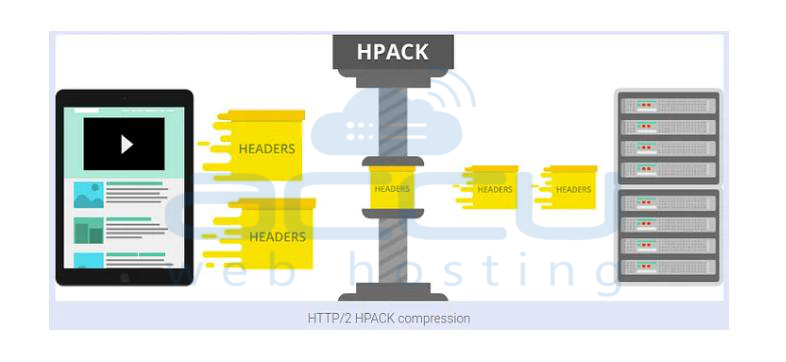
Header compression:
- Smaller files load faster. Both HTTP/1.1 and HTTP/2 make files smaller to speed things up.
- However, HTTP/2 uses a better method called HPACK, which removes extra information from the file headers, saving a few bytes from each file.
- When you add all the files on a webpage, those saved bytes load faster.
Binary Protocol:
- The newest version of HTTP has changed its capabilities significantly, including switching from using words to a language of 1s and 0s, called binary.
- In the older version (HTTP1.x), it used words to perform tasks, but now, in HTTP/2, it uses binary code to do the same thing.
- This makes it simpler because before, tasks had both words and empty spaces, which could be confusing.
- When browsers use HTTP/2, they change the words into binary code before sending them over the internet.
Conclusion:
- HTTP/2 is very pInternetand has a substantial impact on the online world. It gives a lot of control to make web applications work better.
- Even though new technologies like HTTP/3 are being developed to improve HTTP/2, it will still be around for a while.
- The tech world constantly changes; we need advanced technologies to keep up.



